How Hyperautomation Combines AI and Machine Learning for Smarter Workflows

As industries evolve with digital disruption, enterprises are implementing smarter systems to improve efficiency and stay relevant. A key advancement driving this transformation is hyperautomation, a comprehensive approach that integrates tools like machine learning, robotic process automation, and intelligent analytics to automate complex business processes from start to finish. As the demand for agility and scalability grows, gaining a clear understanding of hyperautomation and its capabilities is more important than ever.
How Hyperautomation Works: The Role of AI and Machine Learning
What is hyperautomation? It refers to the use of advanced technologies such as AI, ML, and RPA to automate complex business processes that were previously dependent on human decision-making. It doesn’t stop at automating repetitive tasks; hyperautomation aims to create a fully connected ecosystem where data, analytics, and decision-making work in sync to drive smarter operations.
While traditional automation focuses on rule-based tasks, hyperautomation adds cognitive capabilities, enabling systems to learn, adapt, and improve over time. This makes it a transformative solution across industries, from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and logistics.
For example, in invoice processing, RPA bots may extract data from documents, but AI and ML help categorize, validate, and interpret the information, improving accuracy and speed. This combination leads to smarter workflows that continuously evolve as they learn from new inputs and exceptions.
Automation vs. Hyperautomation: What’s the Difference?
While automation and hyperautomation are often used interchangeably, they refer to different levels of digital transformation. Understanding the hyperautomation vs intelligent automation is essential for businesses aiming to improve efficiency and stay competitive in the age of intelligent technology.
Automation refers to the use of technology to perform repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention. It’s typically rule-based and focuses on individual processes. For example, setting up an automated email responder or using software to generate monthly invoices.
Hyperautomation goes a step further. It involves automating not just tasks, but entire business processes by combining multiple advanced technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Process Mining. The goal is to create a fully automated, intelligent, and self-improving workflow.
2. Technologies Used
Automation
- Rule-based systems
- Basic scripts or macros
- Standalone automation tools (e.g., Excel macros, IFTTT, simple RPA bots)
Hyperautomation
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Process Mining
- Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
- Low-code/No-code platforms
Hyperautomation brings all these technologies together in a unified ecosystem.
3. Level of Intelligence
Automation
- Performs predefined tasks
- Operates on static rules
- Lacks adaptability or decision-making capabilities
Hyperautomation
- Learns and adapts using AI/ML
- Makes intelligent decisions based on data patterns
- Continuously improves through feedback and monitoring
This means hyperautomation can evolve, while traditional automation remains static unless manually updated.
4. Human Involvement
Automation still requires human intervention for setup, monitoring, and exception handling. For instance, if a condition changes or an error occurs, a human often needs to step in.
Hyperautomation minimizes human intervention by including self-correcting and self-learning mechanisms. It can detect anomalies, find alternative workflows, and resolve issues on its own in many cases.
5. Scalability
Automation is limited to specific tasks or departments. It’s harder to scale across an organization without significant manual effort.
Hyperautomation is designed for enterprise-wide scalability. It creates a digital workforce that can be deployed across multiple departments, systems, and processes with minimal configuration.
6. Outcome Focus
Automation is focused on efficiency and time-saving for individual tasks.
Hyperautomation focuses on end-to-end business transformation, driving innovation, agility, and strategic decision-making.
FACT: Hyperautomation significantly improves accuracy in automated processes. Maersk achieved a 97.4% accuracy rate in logistics operations by implementing AI and ML-driven hyperautomation solutions, compared to the previous average of 88%
Example to Illustrate the Difference
- Automation Example: An RPA bot that extracts data from invoices and enters it into an accounting system.
- Hyperautomation Example: A system that not only extracts and processes invoice data but also uses AI to detect fraud, forecast payment schedules, route exceptions to the right department, and continuously optimize the entire accounts payable process.
| Feature | Automation | Hyperautomation |
| Scope | Task-level | End-to-end process |
| Technology | Basic tools, RPA | RPA + AI + ML + NLP + Process Mining |
| Intelligence | Rule-based | Adaptive, learning-based |
| Human Involvement | Moderate | Minimal |
| Scalability | Limited | Enterprise-wide |
| Goal | Efficiency | Digital transformation and agility |
Hyperautomation Tools and Platforms
Several hyperautomation platforms are available today, offering a mix of automation, intelligence, and integration capabilities. Popular hyperautomation tools include:
- UiPath: Offers RPA integrated with AI, process mining, and analytics.
- Automation Anywhere: Known for its cloud-native automation suite with AI and ML support.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Provides low-code tools with AI builder for business users.
- IBM Automation: Offers a complete suite for workflow, RPA, and decision automation.
These platforms allow businesses to create agile and adaptable automation environments, reducing dependency on IT teams and promoting citizen development.
Hyperautomation Use Cases Across Industries
The real power of hyperautomation becomes evident when looking at its diverse use cases. Some prominent hyperautomation examples include:
The true strength of hyperautomation lies in its ability to integrate advanced technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Machine Learning (ML) to create intelligent, adaptive systems. Below are industry-specific use cases that highlight its transformative potential:
Finance: Smarter, Faster, and Safer Financial Operations
In the finance sector, hyperautomation significantly enhances speed, accuracy, and compliance in routine operations:
1- Loan Approval Automation: By integrating AI with RPA, financial institutions can analyze credit scores, income data, and customer history in real time to approve or reject loan applications faster and more accurately.
2- Fraud Detection: Machine learning models can detect patterns and anomalies in transaction data, instantly flagging suspicious activity and triggering automated workflows for investigation.
3- Regulatory Compliance: Automated systems continuously monitor financial transactions and documentation, ensuring compliance with regulations such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering), reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
Healthcare: Improving Care Delivery and Administrative Efficiency
Hyperautomation in healthcare not only improves patient outcomes but also streamlines back-office operations:
1- Patient Data Processing: Automated systems can extract, validate, and update electronic health records (EHRs), minimizing human error and improving access to accurate patient information.
2- Appointment Scheduling: Intelligent bots handle appointment bookings, reminders, and cancellations, optimizing scheduling and reducing no-shows.
3- Diagnostic Workflows: AI-powered tools assist in diagnostics by analyzing medical images, lab reports, and symptoms, helping healthcare providers make faster, data-driven decisions.
Retail: Driving Operational Excellence and Customer Satisfaction
Retailers are embracing hyperautomation to stay competitive in a fast-paced, consumer-driven market:
1- Supply Chain Automation: End-to-end supply chain tracking, automated order processing, and intelligent demand forecasting reduce delays and improve delivery accuracy.
2- Inventory Management: AI algorithms monitor sales trends and stock levels in real time, automating reordering and minimizing overstock or stockouts.
3- Customer Support: Chatbots and virtual assistants, powered by AI, handle customer inquiries, process returns, and provide personalized shopping assistance 24/7.
Manufacturing: Enhancing Productivity and Reducing Downtime
In manufacturing, hyperautomation brings a new level of precision, safety, and scalability to production operations:
1- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors and AI analyze machine data to predict failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
2- Quality Control: Automated vision systems and machine learning algorithms inspect products for defects, ensuring consistent quality and reducing manual labor.
3- Production Optimization: Hyperautomation streamlines scheduling, resource allocation, and workflow management, maximizing throughput and minimizing waste.
Human Resources: Building Smarter Workplaces
HR departments leverage hyperautomation to improve employee experience and operational agility:
1- Resume Screening: AI scans thousands of resumes in seconds, identifying the best-fit candidates based on skills, experience, and job requirements.
2- Onboarding Automation: New employee onboarding is streamlined with automated document processing, training assignments, and account provisioning.
3- Employee Engagement Tracking: Analytics tools track employee satisfaction, productivity, and engagement through surveys and behavioral data, enabling proactive HR interventions.
Benefits of Hyperautomation
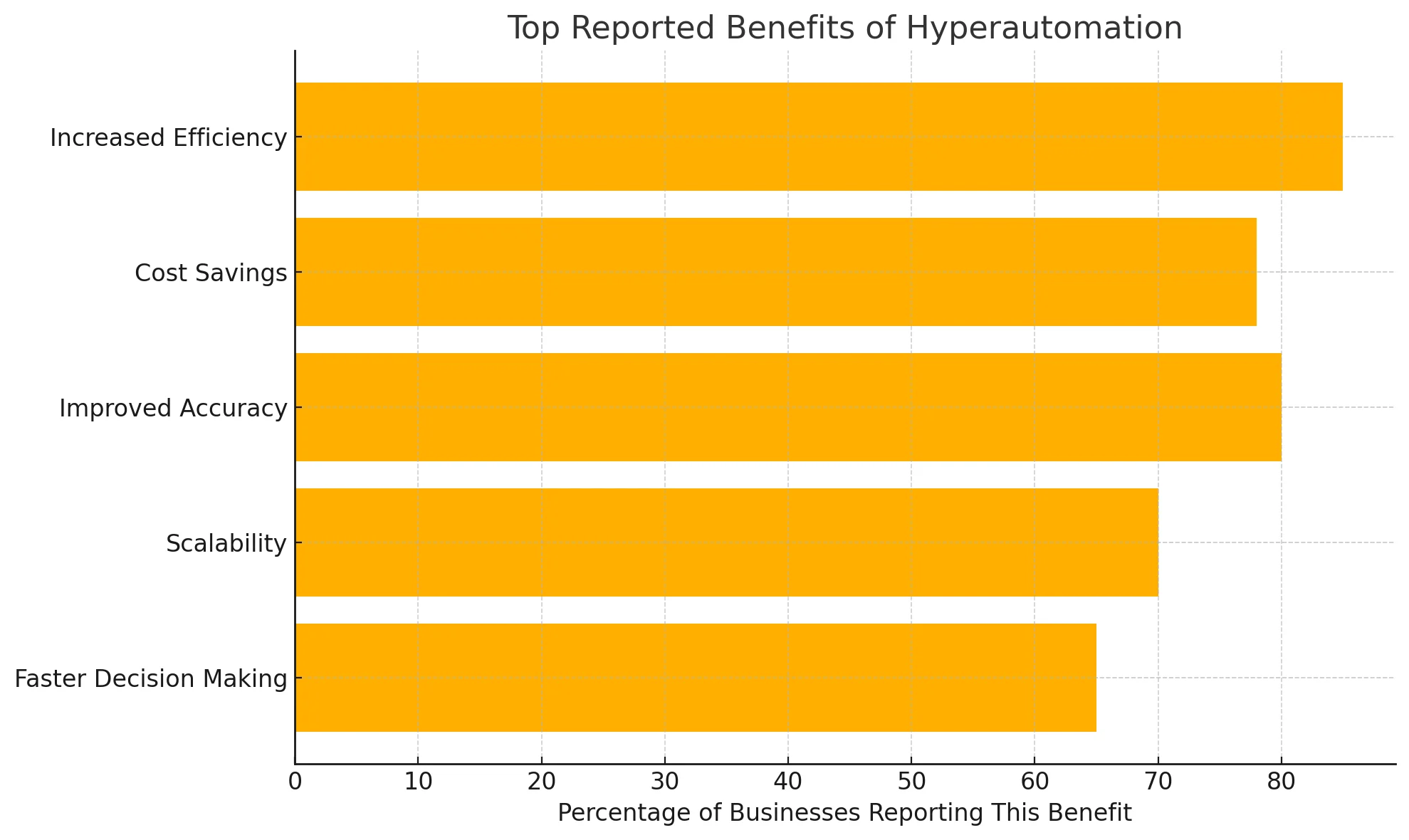
Adopting hyperautomation solutions offers several business advantages:
1- Increased Efficiency
Hyperautomation significantly improves operational efficiency by reducing manual errors and speeding up task execution. Repetitive processes that once took hours can now be completed in minutes, freeing up human workers to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
2- Cost Savings
By automating labor-intensive and time-consuming tasks, businesses can reduce the need for manual intervention, leading to substantial cost savings. This also decreases reliance on outsourced services and minimizes the risk of costly human errors, further lowering operational expenses.
3- Scalability
Hyperautomation enables organizations to scale their operations without the need for a proportional increase in workforce. Intelligent systems can handle growing workloads, process large volumes of data, and adapt to evolving business needs, all without compromising performance or accuracy.
4- Improved Decision-Making
With the integration of AI and machine learning, hyperautomation offers advanced data analytics that deliver real-time insights. These technologies can analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns and trends, empowering decision-makers with accurate, actionable information that enhances strategic planning.
5- Enhanced Customer Experience
Faster response times, accurate data processing, and personalized interactions driven by automation contribute to a seamless customer experience. Chatbots, automated service workflows, and proactive engagement tools help businesses exceed customer expectations, increasing satisfaction and loyalty
When selecting hyperautomation services, organizations should evaluate their current processes and identify areas that would benefit most from automation. The right service provider will offer a tailored approach, combining consulting, platform selection, implementation, and ongoing support. Hyperautomation orchestrates workflows across multiple systems using AI-powered tools. This integration ensures that processes are optimized end-to-end rather than in isolated silos.
Additionally, vendors should have expertise in integrating existing systems and deploying scalable architectures that align with business goals.
Drawbacks of Hyperautomation
While hyperautomation RPA offers significant benefits, it comes with notable drawbacks and challenges that organizations must address to ensure successful implementation. Below are the key disadvantages:
1- High Implementation Costs
Hyperautomation requires substantial investment in advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation (RPA). The costs associated with purchasing software, hardware, training employees, and restructuring processes can be prohibitive for small businesses or organizations with limited resources.
2- Risk of Data Privacy Violations
As hyperautomation often involves handling sensitive customer data across multiple systems, there is a heightened risk of data privacy violations. Organizations must invest in robust security measures like data masking and encryption to mitigate these risks.
3- Dependency on Synthetic Data
Hyperautomation relies on synthetic data sets for training AI models. The unavailability or inadequacy of such data can slow down operations and hinder the effectiveness of automation systems.
4- Bias in AI Systems
AI models used in hyperautomation can inherit biases from their training data or algorithms. These biases may lead to inaccurate predictions or discriminatory outcomes, affecting decision-making processes.
5- Complexity and Oversight Challenges
Managing large-scale hyperautomation systems involving thousands of bots interacting across various platforms can be complex. Ensuring proper oversight, monitoring, and security for these systems is critical but challenging, especially when dealing with sensitive customer data.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation is not just a buzzword; it’s a critical shift in how companies approach digital transformation. By combining AI, machine learning, and RPA, organizations can achieve smarter workflows that boost productivity, cut costs, and enhance agility. Whether you’re exploring hyperautomation tools, evaluating platforms, or identifying use cases in your industry, now is the time to embrace the future of intelligent business operations.







